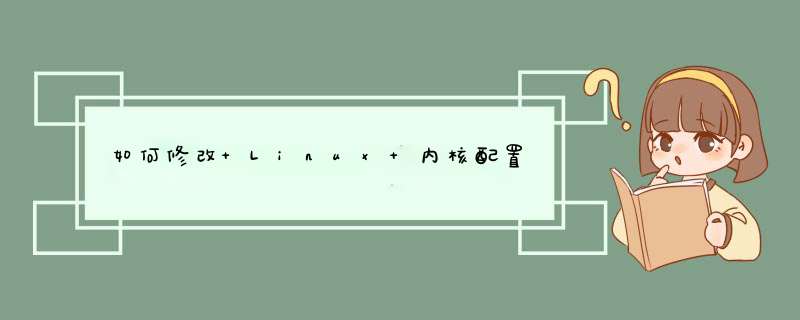
首先打开/etc/sysctl.conf文件,查看如下两行的设置值,这里是:
kernel.shmall
=
2097152
kernel.shmmax
=
4294967295
如果系统默认的配置比这里给出的值大,就不要修改原有配置。同时在/etc/sysctl.conf文件最后,添加以下内容:
fs.file-max
=
6553600
kernel.shmmni
=
4096
kernel.sem
=
250
32000
100
128
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range
=
1024
65000
net.core.rmem_default
=
4194304
net.core.rmem_max
=
4194304
net.core.wmem_default
=
262144
net.core.wmem_max
=
262144
这里的“fs.file-max
=
6553600”其实是由“fs.file-max
=
512
*
PROCESSES”得到的,我们指定PROCESSES的值为12800,即为“fs.file-max
=512
*12800”。
sysctl.conf文件修改完毕后,接着执行“sysctl
-p”使设置生效。
[root@localhost
~]#
sysctl
-p
常用的内核参数的含义如下。
kernel.shmmax:表示单个共享内存段的最大值,以字节为单位,此值一般为物理内存的一半,不过大一点也没关系,这里设定的为4GB,即“4294967295/1024/1024/1024=4G”。
kernel.shmmni:表示单个共享内存段的最小值,一般为4kB,即4096bit.
kernel.shmall:表示可用共享内存的总量,单位是页,在32位系统上一页等于4kB,也就是4096字节。
fs.file-max:表示文件句柄的最大数量。文件句柄表示在Linux系统中可以打开的文件数量。
ip_local_port_range:表示端口的范围,为指定的内容。
kernel.sem:表示设置的信号量,这4个参数内容大小固定。
net.core.rmem_default:表示接收套接字缓冲区大小的缺省值(以字节为单位)。
net.core.rmem_max
:表示接收套接字缓冲区大小的最大值(以字节为单位)
net.core.wmem_default:表示发送套接字缓冲区大小的缺省值(以字节为单位)。
net.core.wmem_max:表示发送套接字缓冲区大小的最大值(以字节为单位)。
帮你修改了一下,编译运行没问题,修改的地方都标出来了,由于不知道你程序的功能,所以没有对你的程序逻辑进行分析
#include <stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<semaphore.h>
#include<unistd.h>
//----------------以下是修改的部分
sem_t in
sem_t out
sem_t handout
sem_t handin
sem_t goout
//----------------
int counter=0
void * studentIn(void *a)
{
sem_wait(&in)//修改
counter++
printf("%d\n",counter)
if(counter==30)
{
sem_post(&handout)//修改
return NULL
}
sem_post(&in)//修改
return NULL
}
void * fteacherhandout(void *b)
{
sem_wait(&handout)//修改
printf("teacher said:hand out over\n")
sem_post(&handin)//修改
return NULL
}
void * studentout(void *c)
{
sem_wait(&handin)//修改
sem_wait(&out)//修改
counter--
printf("%d\n",counter)
if(counter==0)
{
sem_post(&goout)//修改
return NULL
}
sem_post(&out)//修改
}
void * fteacherout(void *d)
{
sem_wait(&goout)//修改
printf("teacher go out")
return NULL
}
void main()
{
int i=0
//----------------以下是修改的部分
sem_init(&in,0,1)
sem_init(&out,0,1)
sem_init(&handin,0,0)
sem_init(&handout,0,0)
sem_init(&goout,0,0)
//----------------
pthread_t thread1[30],thread2[30],teacher1,teacher2
pthread_attr_t attr
pthread_attr_init(&attr)
for(i=0i<30i++)
{
pthread_create(&thread1[i],&attr,studentIn,NULL)
}
for(i=0i<30i++)
{
pthread_create(&thread2[i],&attr,studentout,NULL)
}
pthread_create(&teacher1,&attr,fteacherhandout,NULL)
pthread_create(&teacher2,&attr,fteacherout,NULL)
return
}
/proc/sys/目录下的文件操作方式有三种,1,通过sysctl进行操作,
#sysctl debug.edp.xxxx 显示/proc/sys/debug/edp/xxxx的值
#sysctl -w debug.edp.xxxx=1 将/proc/sys/debug/edp/xxxx值设置为1
2,通过常规的echo和cat等方式操作,
#cat /proc/sys/debug//edp/xxxx 显示文件内容
#echo 1 >/proc/sys/debug//edp/xxxx 修改文件内容
3,系统调用open()/write()等函数操作。
需要通过编程来实现。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:夏雨云

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)